Risk assessments are conducted to determine if a chemical found in the environment is harmful to public health; for example, answering questions such as "does chemical 'x' promote cancer?" Conducting an impartial analysis of chemicals is thus critical to ensure that public policies reflect the best available scientific evidence. Unfortunately, the process of retrieving, extracting, and analyzing findings reported in scientific literature is time consuming and can delay when policies are updated to reflect new evidence.
Professor Catherine Blake and Jodi A. Flaws, professor of comparative biosciences at the University of Illinois, have developed an automated approach that moves beyond the retrieval of relevant literature to the extraction step of the information synthesis process. In a recent study of cell death and proliferation—two fundamental hallmarks of cancer—they demonstrate how simply counting the number of outcomes shows a very different picture than focusing on how key outcomes have changed.
"Systems currently just focus on the retrieval step, and if you base decisions solely on the number of abstracts retrieved, you would make the wrong decision," said Blake. "You have to look at the directionality of the evidence."
The natural language processing (NLP) system that Blake developed scales to over 400,000 abstracts and identifies the directionality of evidence (refuting, neutral, or supporting) for 27 different chemicals. Their approach automates the extraction step, providing researchers with waffle plots that visually present the distribution of supporting, neutral, and refuting evidence for each chemical. For example, in the waffle plots below, chemical 1 has more refuting evidence whereas chemical 22 has more supporting evidence.
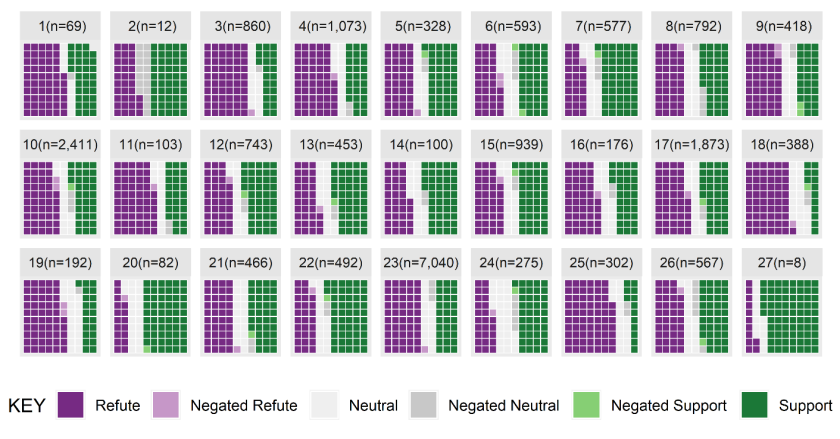
This automated approach provides researchers with important detail that is missing in existing automated systems, which is closer to the manual processes used in decision-making, and also maintains the level of transparency needed in a public policy setting. Blake and Flaws' study, "Using semantics to scale up evidence-based chemical risk-assessments," was recently published in the peer-reviewed open access journal PLOS One.
Blake's research seeks to accelerate science and inform policy by automatically extracting and summarizing claims reported in the scientific literature. She holds a PhD and MS in information and computer science from the University of California, Irvine, and an MS and BS in computer science from the University of Wollongong, Australia.
