The use of data science tools in research across campuses has exploded–from engineering and science to the humanities and social sciences. But there is no established data science discipline and no recognized way for various academic fields to develop and integrate accepted data science processes into research.
Associate Professor Victoria Stodden has proposed a framework for guiding researchers and curriculum development in data science and for aiding policy and funding decisions. She outlines the approach in the journal Communications of the ACM.
Stodden has studied issues of reproducibility of research findings for more than a decade. Now, the widespread use of computational tools for research has initiated discussions about transparency, bias, ethics and other topics. These ideas are broader than any particular field, and researchers from different fields need a common framework for how to approach and talk about them, she said.
Stodden said her approach will help define data science as a scientific discipline in its own right; provide a way to have a common conversation across various disciplines; encourage development of and train researchers and scientists on data-driven research methods; help them to agree on the most important issues in the emerging field of data science; and help consumers of computational research to understand how the results were produced.
"I'm hoping it's a way to unify the conversations going on now–to help them evolve and share knowledge in a way to leverage and learn from what other people are doing–and talk about what's going on across different disciplines," Stodden said.
The framework helps identify which issues can be generalized across disciplines and which are specific to a discipline, she said.
Stodden's proposal builds on the concept of the data life cycle used by information scientists to describe the various stages of a dataset. Her data science life cycle looks at not only datasets, but also the tools of computational research such as computer code and software, as well as the research findings.
The data science life cycle would allow researchers to look at the computational research process from data collection to analysis, validation, dissemination and ultimately how the research findings are used in public policy discussions, she said. It would bring into the conversation concepts of transparency, reproducibility of results, how results are interpreted, potential bias and ethics.
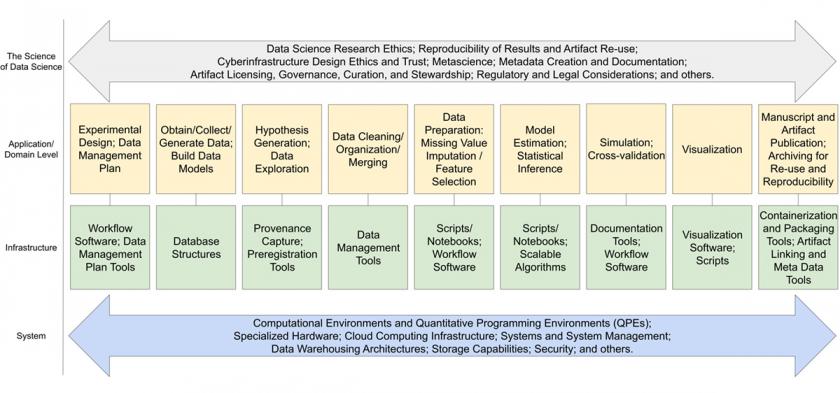
"It's a framework for how to bring all these different topics together and think about what it means to have a field of data science," Stodden said. "With more strategic thinking about what data science means, and what it means to leverage these tools, we will be doing better science."
The data science life cycle recognizes the need for preserving data, software and computational information and making them widely available after results are published, allowing for reproducibility.
Her approach also will help guide the development of a curriculum of data science, she said, providing a way to see where existing courses fit and where new courses may need to be developed.
"For a student seeking to do advanced coursework in data science, it can appear that statistics is not computational enough, computer science isn’t data inference-focused enough, information science is too broad, and the domain sciences don’t provide a broad enough pedagogical agenda in data science," she wrote.